Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?
What is the full form of RO UV and UF? | RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?

Today we are going to provide you all a lot of information about RO, UV, and UF (What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?) through this article like what it is and what is their full form.
To get information about this, all of you will have to read this article till the end because in this article we have given information related to it, only by reading it you will be able to know about it, so please do read this article till the end.
RO: Reverse Osmosis
The full form of RO is Reverse Osmosis. It is a process that helps RO water purifiers remove unwanted ions, dissolved solids, and TDS from the water. In osmosis, the solvent passes from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution.
In reverse osmosis (RO), the solvent passes through a semipermeable membrane in the opposite direction (from a more concentrated solution to a less concentrated solution). “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
RO can remove a wide variety of dissolved and suspended chemical species, as well as biological species (mainly bacteria), from water, and is used in industrial processes and in the production of drinking water.
Also Read:
- Difference Between Oven and Microwave – Which Reigns Supreme in Your Kitchen?
- How To Filter Water at Home? Top 5 Easy and Effective Ways to Purify Water
- Top 15 Best Refrigerators in India 2023 | Best Refrigerators Under 25000
- What are RO and Uf in a water purifier – Reverse Osmosis Water | Difference Between ro and Aquaguard
Most commonly around the world, RO is used in domestic drinking water purification systems and for improving drinking water. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Other Full Forms of RO Abbreviation
- Ragnarok Online
- radiation oncology
- Romania
- Renal Osteodystrophy
- Romanian
- Results Of
- read-only
- rule out
- Regional Office
- roll on
- rollover
- Research Organization
- right on
- Ring Out
- Registered owner
- Room Only
- Repair and Overhaul
- Red Orchestra
- Responsible officer
- routine orders
What is RO?

So friends, first of all, tell all of you that the full form of RO is Reverse Osmosis, which is also known as Viparit Parasaran in Hindi. It is a type of process in which unwanted ions, dissolved solids, and TDS are separated from water.
Because of this, the water becomes pure, that is, all the impurities inside the water get separated. In the process of reverse osmosis, the solvent moves in the opposite direction through a semi-permeable membrane. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
During this process, with the help of aro, the impure water goes inside the water purifier and then its impurity is separated by a pump. Then after that, we get pure water from that water purifier.
Get the Best Aquaguard water purifier – Click Here
Benefits of RO
RO, or Reverse Osmosis, is a water purification process that uses a partially permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from water. It’s commonly used in various applications for water treatment and purification. Here are some benefits of using reverse osmosis:
Highly Effective Filtration:
RO is highly effective in removing a wide range of contaminants from water, including dissolved salts, minerals, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and even some organic molecules.
This makes it an excellent choice for producing clean and safe drinking water. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Improved Taste and Odor:
The removal of impurities often leads to improved taste, odor, and appearance of water. RO can greatly enhance the quality of water for drinking and cooking purposes.
Health and Safety:
Reverse osmosis can effectively remove harmful substances such as lead, arsenic, fluoride, and other contaminants that can be detrimental to human health. This is especially important in areas with poor water quality.
Compact and Modular:
RO systems can be designed to fit various sizes and scales, from small under-sink units in homes to larger systems for commercial or industrial applications. This flexibility makes it suitable for different contexts.
Energy Efficiency:
While RO does require energy to push water through the membrane, modern advancements have made the process more energy-efficient over the years. Energy recovery devices, such as pressure exchangers and permeate pumps, can help minimize energy consumption. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Wastewater Reduction:
While RO produces purified water, there is also a byproduct stream of concentrated contaminants, often referred to as brine or reject water. In some systems, this waste stream can be minimized through innovative designs and the use of technologies like “zero liquid discharge,” reducing environmental impact.
Versatility:
Reverse osmosis can be used for various applications beyond drinking water, including desalination of seawater, production of ultrapure water for industrial processes, and treatment of wastewater for reuse.
Low Chemical Usage:
Compared to some other water treatment methods, RO typically requires fewer chemicals. This can be seen as a benefit in terms of environmental impact and reduced chemical handling. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Consistency:
RO systems provide consistent water quality regardless of the source water variability. This makes it a reliable choice for maintaining a consistent supply of purified water.
Reduced Maintenance:
RO systems generally have fewer moving parts and require less maintenance compared to some other water treatment systems. Regular maintenance mainly involves changing filters and occasionally cleaning the membrane.
Environmental Benefits:
In regions where access to clean water is a challenge, RO can provide a sustainable solution by purifying available water sources, reducing the need for bottled water, and decreasing reliance on environmentally damaging practices.
However, it’s important to note that while RO offers many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks to consider, such as energy requirements, wastewater production, and the removal of beneficial minerals along with contaminants.
The suitability of RO depends on specific needs, water quality, and environmental considerations. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
UV: Ultraviolet

The full form of UV is Ultraviolet. In RO water purifiers, the reverse osmosis process can eliminate solid and dissolved ions, but cannot kill bacteria or germs in the water. UV rays can kill these bacteria and germs. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Therefore, in most RO water purifiers, the water goes through a tube and is exposed to UV radiation which kills harmful bacteria and germs. UV technology does not contain chemicals and is easy to maintain. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
UV radiation was discovered in 1801. It is electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths from 10 nm (with a uniform frequency of about 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), which is shorter than that of visible light. But is bigger than an X-ray.
UV radiation is present in sunlight and makes up about 10% of the total output of electromagnetic radiation from the Sun. It is produced by electric arcs and special lights, such as mercury vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights.
Other Full Forms of UV Abbreviation
- Universidad Veracruzana
- unit price
- Ultra Violence
- Unión Valenciana
- urine volume
- User Visible
- user variables
- Underwater Vessel
- Unemployment and Vacancy
- Unite de Villegiature
- Unpleasant Visual
- ultra visual
- Uncle Vernon
- United Videos
- Unnamed Volcanics
- ultra vires
- Unique Voice
- Upper Volta
- Unique visitors
- Ultra Violator
What is UV?
So friends, first of all, let us tell you that the full form of UV is ultraviolet. So friends, as we told you the process of ARO i.e. reverse osmosis is called what happens inside the water purifier.
Under this process, the water purifier removes unwanted ions, dissolved solids, and TDS from the water, but it is unable to kill germs and bacteria from the water.
That’s why there is a tube in the water purifier through which water passes and that water comes in contact with UV due to which bacteria and germs die from the water. Let us also tell everyone that UV does not contain any kind of chemical. UV radiation was discovered in 1801.
Benefits of UV
Certainly, here are the benefits of using ultraviolet (UV) disinfection:
Effective Microorganism Elimination:
UV radiation effectively destroys or inactivates a wide range of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites, preventing their reproduction and the spread of waterborne diseases.
Chemical-Free Process:
UV disinfection doesn’t involve the use of chemicals, making it a safe and environmentally friendly method. It doesn’t introduce any harmful byproducts into the water.
Quick Treatment:
UV treatment is rapid and doesn’t require a long contact time, unlike some chemical disinfection methods. Water can be disinfected almost instantly as it passes through the UV chamber.
No Residual Taste or Odor:
Unlike some chemical disinfectants, UV treatment doesn’t leave behind any taste, odor, or color in the water. This ensures that the water’s natural characteristics are preserved.
Low Maintenance:
UV systems are relatively simple and require minimal maintenance. Regular maintenance usually involves replacing the UV lamp and periodic cleaning of the quartz sleeve to ensure optimal performance.
Continuous Disinfection:
UV systems can operate continuously without the need for shutdowns or downtime. This ensures a constant supply of disinfected water without interruptions.
Safe for Drinking Water:
UV disinfection is approved for drinking water treatment by regulatory agencies like the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
Compact and Space-Efficient:
UV systems are often compact and can be easily integrated into existing water treatment systems, making them suitable for a variety of applications and settings.
Minimal Impact on Water Chemistry:
UV treatment doesn’t alter the chemical composition of water or remove beneficial minerals, maintaining the water’s overall quality.
Applicable to Various Water Sources:
UV treatment can be used with various water sources, including well water, surface water, and municipal water supplies, effectively targeting a broad spectrum of contaminants.
Cost-Effective:
While initial installation costs might vary, UV systems generally have lower operational costs compared to ongoing expenses associated with chemical disinfection methods.
Safety and Operator-Friendly:
UV disinfection doesn’t pose significant risks to operators or require special training for handling hazardous chemicals.
Complements Other Treatment Methods: UV disinfection can be used in combination with other water treatment methods, such as filtration, to create a comprehensive water purification system.
Reliable Performance:
UV systems have a high degree of reliability when properly maintained, providing consistent disinfection performance over time.
It’s important to note that UV disinfection is particularly effective against microorganisms but might not remove other types of contaminants like dissolved solids, chemicals, or particles. As such, its effectiveness should be considered in conjunction with the specific water quality challenges being addressed.
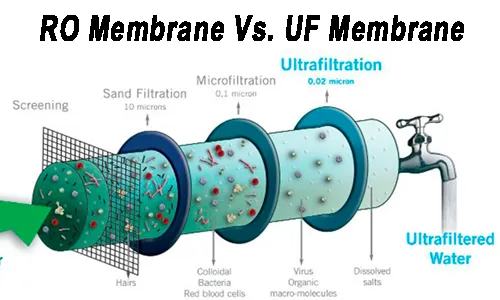
UF: Ultrafiltration
The full form of UF is Ultrafiltration. This is a type of membrane filtration used in UF water purifiers. UF technology works without electricity and aerates suspended solids, particles, and larger water molecules through a hollow membrane. In this technique, water is passed through a semipermeable membrane with a hollow fiber thread.
Large particles and suspended solutes are retained and water passes through the membrane. UF happens before RO filtration before the water enters the water purifier.
“What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference” UF reduces the load on the RO membrane and extends the life of the membrane. By using UF, you cannot convert hard water into soft water, which is what an RO purifier can provide clean RO water.
Other Full Forms of UF Abbreviation
- University of Florida
- Used For
- User Friendly
- Unidad De Fomento
- Uncertainty Factor
- Undocumented Features
- Ultimate Force
- Underground Feeder
- Utter Failure
- Upper Freehold
- United Free
- Unstoppable Force
- Ultra Fly
- UltraFlex
- Unrolling Factor
- Usable Feeders
- Undulation Factor
- Untersuchungsführer
- Ultrahigh Frequency
- Underground Fighters
- Upper Feasibility
- Urban Fantasy
What is UF?
So friends, first of all, let us tell you that the full form of UF is Ultrafiltration. Let us also tell you that this is a type of membrane filtration that is in UF water purifiers. “What is the full form of RO UV and UF?, RO-UV-UF Full Form and Difference?”
Let us also tell you that this type of water park can run without any electricity. In this type of water purifier, water is passed through a hollow fiber threaded semi-permeable membrane.
During this suspended solids, particles, and larger water molecules are removed from the water. The process of ultrafiltration is done before the filtration process of RO. UF extends the life of the membrane.
Benefits of UF
Certainly, here are the benefits of using Ultrafiltration (UF) for water treatment:
Effective Particle Removal: Ultrafiltration is highly effective at removing suspended particles, colloids, bacteria, viruses, and some macromolecules from water. This leads to improved water clarity and reduced turbidity.

Physical Barrier Process:
UF operates on a physical separation principle, using semi-permeable membranes with specific pore sizes to block contaminants while allowing water and smaller molecules to pass through. It doesn’t involve chemicals, ensuring a natural treatment process.
Microorganism Removal:
UF membranes can effectively remove bacteria and larger viruses, contributing to the reduction of waterborne diseases and improving overall water quality.
Consistent Performance:
UF systems provide consistent and reliable performance over time, ensuring a stable supply of treated water.
Low Operating Pressure: UF typically operates at lower pressures compared to some other membrane processes like Reverse Osmosis, which can lead to energy savings and reduced operational costs.
Suitable for Low Turbidity Water:
UF can effectively treat water with low to moderate turbidity, making it well-suited for treating surface water, well water, and even wastewater before further treatment.
Chemical-Free Filtration:
UF doesn’t require the addition of chemicals for particle removal, reducing the environmental impact and the need for chemical handling.
Tolerant to Feed Water Variability:
UF systems can handle variations in feed water quality and flow rates, making them adaptable to changing water conditions.
Preservation of Essential Minerals:
Unlike some other water treatment methods, UF doesn’t remove beneficial minerals from water, ensuring that the treated water retains its natural composition.
Flexible Design and Scalability:
UF systems can be designed for various flow rates and capacities, making them suitable for both small-scale and large-scale applications.
Pre-Treatment for Other Processes:
UF can serve as an effective pre-treatment step for processes like Reverse Osmosis, protecting RO membranes by removing larger particles that could clog or foul the RO system.
Reduced Risk of Fouling:
UF membranes are less prone to fouling (clogging) compared to finer membrane processes, thanks to the larger pore sizes. However, regular maintenance is still essential.
Waste Minimization:
The waste produced in UF is primarily the concentrated particles and contaminants removed by the membrane, which can be further treated or managed without producing large volumes of wastewater.
Applicable in Various Industries:
UF is used in a wide range of applications, including drinking water treatment, industrial processes, wastewater treatment, and more.
Improved Water Aesthetics:
UF can improve the visual appearance of water by removing suspended particles that might cause cloudiness or discoloration.
It’s important to note that while UF is highly effective at removing suspended particles and microorganisms, it might not be suitable for removing dissolved contaminants like salts or certain chemicals. The selection of the appropriate treatment technology should be based on the specific water quality challenges and treatment objectives.
Defrance Between Ro, UV, and UF

You seem to be asking about various water treatment technologies such as RO (reverse osmosis), UV (ultraviolet), and UF (ultrafiltration). These are all methods of treating and purifying water, but they operate slightly differently and target different types of contaminants. I will briefly describe each of them.
Reverse Osmosis (RO):
Reverse osmosis is a water purification process that uses semipermeable membranes to remove various contaminants from water. Water passes through a membrane under pressure and the membrane blocks particles, ions, and molecules larger than water molecules.
This effectively removes impurities such as dissolved salts, minerals, heavy metals, and other large particles to produce clean, pure water. RO is commonly used for both domestic and industrial water treatment.
Ultraviolet (UV) cleaning:
UV purification uses ultraviolet light to disinfect water by inactivating or destroying microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. UV light destroys the DNA of these microorganisms, stopping them from multiplying and rendering them harmless.
It is important to note that UV cleaning does not remove other contaminants such as dissolved solids, chemicals, or particles. Therefore, it is often used in combination with other filtration methods such as reverse osmosis and activated carbon to provide comprehensive water treatment.
Ultrafiltration (UF):
Ultrafiltration is a physical filtration process that uses semipermeable membranes with larger pores than RO membranes. UF can effectively remove suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, and large molecules from water, but may pass some small dissolved salts and ions.
This process is particularly suitable for treating highly turbid water and removing pathogens. UF is often used as a pretreatment step in RO systems or as an independent purification method for drinking water.
In total:
RO primarily removes dissolved salts, minerals, heavy metals, and other contaminants. UV disinfects water by inactivating microorganisms, but it does not remove other contaminants.
UF removes large particles, bacteria, and viruses, but may allow some small solutes to pass through.
The choice of water treatment technology depends on the specific contaminants in the water and the level of treatment required to meet quality standards. In some cases, these techniques can be used in combination to provide comprehensive water purification.
Conclusion: What is the full form of RO, UV, and UF?
In conclusion, understanding the full forms and functions of RO, UV, and UF in the context of water purification is essential for making informed decisions about water treatment.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) stands as a cornerstone of comprehensive purification, effectively eliminating a wide spectrum of contaminants and minerals through a semipermeable membrane.
Ultraviolet (UV) purification employs the power of light to neutralize harmful microorganisms, offering a reliable disinfection method that doesn’t alter the water’s chemistry. Ultrafiltration (UF), on the other hand, utilizes a membrane to sieve out particles, bacteria, and some viruses, striking a balance between coarse and fine filtration.
Each method brings distinct advantages to the table, and the synergy between these technologies can enhance the overall quality of treated water. From the precision of RO to the simplicity of UV and the intermediary role of UF, these methods cater to various purification needs.
As consumers, it’s imperative to recognize the strengths and limitations of each technique, enabling us to tailor water purification solutions to our unique contexts.
Whether it’s for home use or industrial applications, the choice of RO, UV, or UF should align with the composition of the water source and the specific contaminants to be addressed.
By delving into the world of water purification, we empower ourselves to make healthier choices and contribute to a safer and more sustainable water supply for all.
FAQs About What is the full form of RO UV and UF?
The full form of RO is Reverse Osmosis.
The full form of UV is Ultraviolet.
The full form of UF is Ultrafiltration.
- Renal Osteodystrophy
- read-only
- rule out
- Regional Office
- roll-on
- rollover
- right on
- Ring Out
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water purification process that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from water. It is commonly used to improve the quality of drinking water by removing contaminants.
Ultraviolet (UV) purification is a method of water treatment that uses ultraviolet light to disinfect water by deactivating bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms present in the water. UV light disrupts the DNA of these microorganisms, preventing them from reproducing and causing diseases.
Ultrafiltration (UF) is a filtration process that uses a semipermeable membrane to separate particles and macromolecules from water. UF is effective in removing suspended solids, colloids, bacteria, and some viruses from water, providing a level of purification between microfiltration and nanofiltration.
These purification methods are commonly used in water treatment systems for domestic and industrial purposes. RO is often used for drinking water purification, UV is used for disinfection in water treatment plants and some point-of-use devices, and UF is used in various applications, including pre-treatment for RO systems and water clarification processes.
Yes, these methods can be used in combination to enhance water purification. For example, some water purifiers use a combination of RO and UV or UF and UV to ensure the comprehensive removal of contaminants and microorganisms.
The choice of method depends on the quality of your water source and the specific contaminants you want to remove. RO is effective for removing a wide range of contaminants, including dissolved salts.
UV is excellent for disinfection, while UF is suitable for removing larger particles and microorganisms. It’s best to analyze your water’s composition and consult with experts to determine the most suitable purification method for your needs.
Each method has its limitations. RO systems can waste water during the purification process. UV systems require electricity and don’t remove non-living contaminants. UF may not effectively remove all dissolved substances. Proper maintenance and system selection are crucial to address these limitations.
Remember that selecting the appropriate purification method depends on your specific water quality concerns and requirements.
Thanks to visit TrustWelly.com

